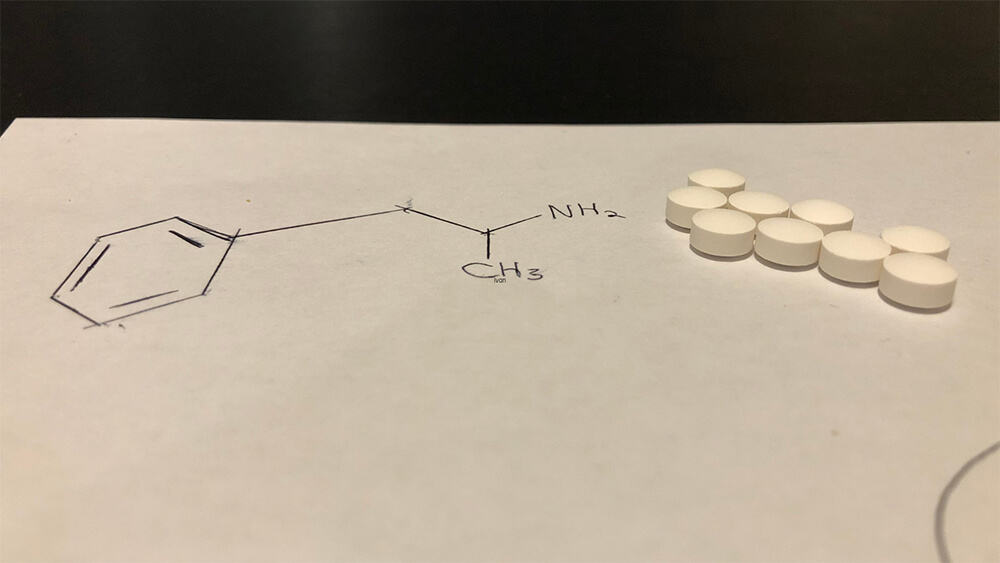
What is Adderall®, and what conditions does it treat?
Adderall® is the brand name for dextroamphetamine-amphetamine, a Schedule II prescription medication that is a central nervous system stimulant.[1]
Adderall® is a combination of two stimulants: amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. It’s taken by mouth in a tablet.
You’re most likely to have Adderall® prescribed for you for one of these two conditions:
- ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
- Narcolepsy, which is a specific type of sleep disorder
Adderall® may be prescribed to you off-label for these conditions[2]:
- Depression, especially when the condition hasn’t improved with other medications
- Anxiety, especially when present with ADHD
- Bi-polar disorder, typically combined with other medications
- Obesity, you should take Adderall® for weight loss only under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
How does Adderall® work?
Adderall® increases the levels of the neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine in your brain. In people with ADHD, those chemicals may be present at lower levels than what’s needed for concentration, motivation, attention, focus, and behavior.
If you have narcolepsy, those neurotransmitters make you more alert and less likely to have a sudden attack of sleep or sleepiness.
Does Adderall® Have Long-Term Effects?
Adderall® can have long-term effects even when used as prescribed, though risks are increased with misuse or prolonged use.
Long-term effects of Adderall® include:
- Adderall® addiction. As noted above, Adderall®, like many stimulants, can be addictive.
- Adderall® withdrawal. If you suddenly stop taking Adderall®, you may feel depressed, be unable to sleep, or feel unusually tired.
- Cardiovascular issues. Adderall® used for an extended time can cause you to have cardiovascular problems, including heart disease and high blood pressure.
- Mental health problems. Some people who use Adderall® for an extended period of time experience mental health issues, including psychosis, depression, and anxiety.
- Cognitive issues. Studies show that long-term use of Adderall® can create problems with your ability to think clearly, make decisions, remember things, and focus your attention.
- Suppressed growth in children. Adderall® has been associated with suppressed growth in children.
What’s important to know about Adderall® for people in recovery from substance abuse disorder?
The decision of whether to take Adderall® while in treatment for substance abuse disorder is important. Take Adderall® only if your healthcare professional specifically prescribes it and after you have fully informed them of any history of addiction you have. They may recommend other treatments or medications.
If it is prescribed to you while you’re in treatment, be sure to take it exactly as directed.
Failure to do so can negatively impact you legally and health-wise and interfere with your recovery in several ways, including:
Your Legal Standing: Using Adderall® without a prescription is illegal and could result in life-altering legal ramifications.
Your Health: Adderall® can have long-term effects that negatively impact your health. See the section below on Adderall® long-term effects.
Your Recovery: When you’re in treatment for substance abuse disorder, Adderall® can slow or derail your recovery process in the following ways:
- Adderall® affects brain chemistry in ways that can be reinforcing and may pose a risk for individuals with a history of substance abuse, potentially impacting recovery.
- Adderall® can be addictive. If you already have a tendency for substance addiction, you’re susceptible to becoming addicted to Adderall®.
- Adderall® can mask other important issues. Changes in your mood, ability to focus, and behavior from Adderall® can make it so that you or recovery professionals aren’t aware of issues like anxiety or depression that should be addressed.
- Adderall® can affect your sleep. You may not be able to sleep well while taking Adderall®, which can mean that you don’t have the physical and emotional reserves needed to fully recover from substance abuse disorder.
How long does it take for Adderall® to start working, and how long do its effects last?
How long it takes for Adderall® to start working for you depends on several factors, including the dose, how it’s formulated, your weight, metabolism, age, and any medical conditions you have.
You’ll typically feel the effects of Adderall® in about half an hour or an hour after you take it and continue to feel those effects for 4-6 hours.
There is a type of Adderall® that releases the drug in a gradual manner over time. The extended-release form of Adderall® (Adderall XR®) typically starts working within 30 minutes to an hour, with its effects lasting up to 10-12 hours.
How does Adderall® make you feel?
If you have ADHD, when Adderall® increases your dopamine levels, you can expect to feel more focused, alert, and able to pay attention. Notice if you’re able to complete tasks for school or more easily.
You may feel as if you have more energy than when you’re not taking it. And you may feel you’re in a more positive mood or feel more confident. You may also feel you need to eat and sleep less than usual. Your heart rate and blood pressure may become elevated as well.
Long-term use of Adderall®, even as prescribed, can lead to tolerance, where higher doses might be needed to achieve the same effect. Misuse increases the risk of addiction.
How will you know whether Adderall® is working for you?
The way you’ll know whether Adderall® is working for you is by answering these questions:
Are your symptoms improving?
- For example, if you have ADHD, are you finding it easier to focus and complete tasks?
- Are you more able to manage your impulses?
- If you have narcolepsy, are you finding that you’re not having times – or having fewer times – when you suddenly fall asleep?
Is your quality of life improving?
- Are you able to complete more tasks for school or work?
- Are you finding that your interactions with friends and family are improving?
- Are you feeling better about yourself?
If you’ve experienced side effects from Adderall®, are they subsiding?
- Look at the list of Adderall®’s possible side effects below. Have you had any of those?
- And if so, have they gotten worse or better?
- Usually, people who experience side effects from Adderall® find that over time they become more manageable or go away completely.
How do you know if you’re taking the correct dose?
Adderall® isn’t a one-dose, one-formulation fits all medications. It may take some time to find the right dose and formulation for you.
Describe how you’re feeling and any side effects you’re experiencing to your prescribing healthcare professional. They’ll work with you to find what works best.
How should you take Adderall®?
Take Adderall® exactly as your healthcare provider directs. If you take too much or too little of it, you may not get relief from your symptoms, or you may experience more side effects.
Take Adderall® at the same time each day. That helps maintain a consistent level in your system.
Take it early in the day. If you take it late in the day or in the evening, your sleep cycle can be disrupted.
If you have ADHD, you may struggle with keeping a schedule for your medications. Use a calendar, an alarm on your phone or watch, or use a pillbox to help you stay on schedule.
What Are The Common Side Effects Of Adderall®?
The most common side effects include[3]:
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Elevated heart rate
- Feeling irritable
- Feeling nervous or restless
- Headache
- High blood pressure
- Insomnia
- Reduced appetite
- Upset stomach
Can there be serious side effects from Adderall®?
Yes. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these side effects:
- Breathing difficulty
- Chest pain
- Hallucinations
- Thoughts of suicide